Docker搭建Kafka
编辑
一、kafka简单介绍
1、kafka简介
Kafka是最初由Linkedin公司开发,是一个分布式、支持分区的(partition)、多副本的(replica),基于zookeeper协调的分布式消息系统,它的最大的特性就是可以实时的处理大量数据以满足各种需求场景:比如基于hadoop的批处理系统、低延迟的实时系统、storm/Spark流式处理引擎,web/nginx日志、访问日志,消息服务等等,用scala语言编写,Linkedin于2010年贡献给了Apache基金会并成为顶级开源 项目。
2、kafka特性
高吞吐量、低延迟:kafka每秒可以处理几十万条消息,它的延迟最低只有几毫秒,每个topic可以分多个partition, consumer group 对partition进行consume操作。
可扩展性:kafka集群支持热扩展
持久性、可靠性:消息被持久化到本地磁盘,并且支持数据备份防止数据丢失
容错性:允许集群中节点失败(若副本数量为n,则允许n-1个节点失败)
高并发:支持数千个客户端同时读写
3、kafka使用场景
日志收集:一个公司可以用Kafka可以收集各种服务的log,通过kafka以统一接口服务的方式开放给各种consumer,例如hadoop、Hbase、Solr等。
消息系统:解耦和生产者和消费者、缓存消息等。
用户活动跟踪:Kafka经常被用来记录web用户或者app用户的各种活动,如浏览网页、搜索、点击等活动,这些活动信息被各个服务器发布到kafka的topic中,然后订阅者通过订阅这些topic来做实时的监控分析,或者装载到hadoop、数据仓库中做离线分析和挖掘。
运营指标:Kafka也经常用来记录运营监控数据。包括收集各种分布式应用的数据,生产各种操作的集中反馈,比如报警和报告。
流式处理:比如spark streaming和storm
事件源
二、docker里kafka的搭建
1、拉取镜像文件
首先去docker镜像仓库拉取kafka镜像,仓库地址:https://hub.docker.com
拉取kafka镜像命令
docker pull wurstmeister/kafka2、挂载宿主机的配置文件
kafka镜像内配置文件路径:/opt/kafka/config
宿主机配置文件路径:/docker/kafka/config
注:配置文件,你可以选择拷贝容器里的配置文件出来到宿主机,后续定制化修改,也可以直接从官网下载kafka安装包,解压后有默认配置文件。
启动kafka命令
docker run -d --restart=always --name kafka -p 9092:9092 \
--link zookeeper \
--env KAFKA_ZOOKEEPER_CONNECT=zookeeper:2181 \
--env KAFKA_LISTENERS=PLAINTEXT://0.0.0.0:9092 \
--env KAFKA_ADVERTISED_LISTENERS=PLAINTEXT://192.168.8.201:9092 \
-v /etc/localtime:/etc/localtime \
-v /home/docker/kafka/data:/kafka \
-v /home/docker/kafka/logs:/opt/kafka/logs \
wurstmeister/kafkaKAFKA_ZOOKEEPER_CONNECT --配置zk注册中心
KAFKA_LISTENERS --需要开启外部访问,LISTENERS直接配置0.0.0.0:9092
KAFKA_ADVERTISED_LISTENERS --为宿主机器的IP地址,如果不这么设置,可能会导致在别的机器上访问不到
同时可以选择挂载宿主机的配置文件和数据存储目录
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
# see kafka.server.KafkaConfig for additional details and defaults
############################# Server Basics #############################
# The id of the broker. This must be set to a unique integer for each broker.
broker.id=-1
############################# Socket Server Settings #############################
# The address the socket server listens on. It will get the value returned from
# java.net.InetAddress.getCanonicalHostName() if not configured.
# FORMAT:
# listeners = listener_name://host_name:port
# EXAMPLE:
# listeners = PLAINTEXT://your.host.name:9092
listeners=PLAINTEXT://0.0.0.0:9092
# Hostname and port the broker will advertise to producers and consumers. If not set,
# it uses the value for "listeners" if configured. Otherwise, it will use the value
# returned from java.net.InetAddress.getCanonicalHostName().
advertised.listeners=PLAINTEXT://192.168.8.201:9092
# Maps listener names to security protocols, the default is for them to be the same. See the config documentation for more details
#listener.security.protocol.map=PLAINTEXT:PLAINTEXT,SSL:SSL,SASL_PLAINTEXT:SASL_PLAINTEXT,SASL_SSL:SASL_SSL
# The number of threads that the server uses for receiving requests from the network and sending responses to the network
num.network.threads=3
# The number of threads that the server uses for processing requests, which may include disk I/O
num.io.threads=8
# The send buffer (SO_SNDBUF) used by the socket server
socket.send.buffer.bytes=102400
# The receive buffer (SO_RCVBUF) used by the socket server
socket.receive.buffer.bytes=102400
# The maximum size of a request that the socket server will accept (protection against OOM)
socket.request.max.bytes=104857600
############################# Log Basics #############################
# A comma separated list of directories under which to store log files
log.dirs=/kafka/kafka-logs-2a55893bad6f
# The default number of log partitions per topic. More partitions allow greater
# parallelism for consumption, but this will also result in more files across
# the brokers.
num.partitions=1
# The number of threads per data directory to be used for log recovery at startup and flushing at shutdown.
# This value is recommended to be increased for installations with data dirs located in RAID array.
num.recovery.threads.per.data.dir=1
############################# Internal Topic Settings #############################
# The replication factor for the group metadata internal topics "__consumer_offsets" and "__transaction_state"
# For anything other than development testing, a value greater than 1 is recommended for to ensure availability such as 3.
offsets.topic.replication.factor=1
transaction.state.log.replication.factor=1
transaction.state.log.min.isr=1
############################# Log Flush Policy #############################
# Messages are immediately written to the filesystem but by default we only fsync() to sync
# the OS cache lazily. The following configurations control the flush of data to disk.
# There are a few important trade-offs here:
# 1. Durability: Unflushed data may be lost if you are not using replication.
# 2. Latency: Very large flush intervals may lead to latency spikes when the flush does occur as there will be a lot of data to flush.
# 3. Throughput: The flush is generally the most expensive operation, and a small flush interval may lead to excessive seeks.
# The settings below allow one to configure the flush policy to flush data after a period of time or
# every N messages (or both). This can be done globally and overridden on a per-topic basis.
# The number of messages to accept before forcing a flush of data to disk
#log.flush.interval.messages=10000
# The maximum amount of time a message can sit in a log before we force a flush
#log.flush.interval.ms=1000
############################# Log Retention Policy #############################
# The following configurations control the disposal of log segments. The policy can
# be set to delete segments after a period of time, or after a given size has accumulated.
# A segment will be deleted whenever *either* of these criteria are met. Deletion always happens
# from the end of the log.
# The minimum age of a log file to be eligible for deletion due to age
log.retention.hours=168
# A size-based retention policy for logs. Segments are pruned from the log unless the remaining
# segments drop below log.retention.bytes. Functions independently of log.retention.hours.
#log.retention.bytes=1073741824
# The maximum size of a log segment file. When this size is reached a new log segment will be created.
log.segment.bytes=1073741824
# The interval at which log segments are checked to see if they can be deleted according
# to the retention policies
log.retention.check.interval.ms=300000
############################# Zookeeper #############################
# Zookeeper connection string (see zookeeper docs for details).
# This is a comma separated host:port pairs, each corresponding to a zk
# server. e.g. "127.0.0.1:3000,127.0.0.1:3001,127.0.0.1:3002".
# You can also append an optional chroot string to the urls to specify the
# root directory for all kafka znodes.
zookeeper.connect=zookeeper:2181
# Timeout in ms for connecting to zookeeper
zookeeper.connection.timeout.ms=6000
# The following configuration specifies the time, in milliseconds, that the GroupCoordinator will delay the initial consumer rebalance.
# The rebalance will be further delayed by the value of group.initial.rebalance.delay.ms as new members join the group, up to a maximum of max.poll.interval.ms.
# The default value for this is 3 seconds.
# We override this to 0 here as it makes for a better out-of-the-box experience for development and testing.
# However, in production environments the default value of 3 seconds is more suitable as this will help to avoid unnecessary, and potentially expensive, rebalances during application startup.
group.initial.rebalance.delay.ms=0
port=9092可以用Kafka Tools来查看消息队列情况
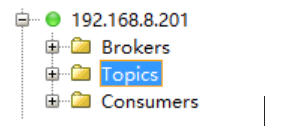
查看所有topic列表
bin/kafka-topics.sh --zookeeper zookeeper:2181 --list- 0
- 0
-
赞助
 赞赏
赞赏
-
分享
